Publications
Filter
Year
Antibacterial and high-performance bioplastics derived from biodegradable PBST and lignin
This study contributes to the conversion of lignin into multifunctional composites with potential antioxidant and antimicrobial applications. Read more

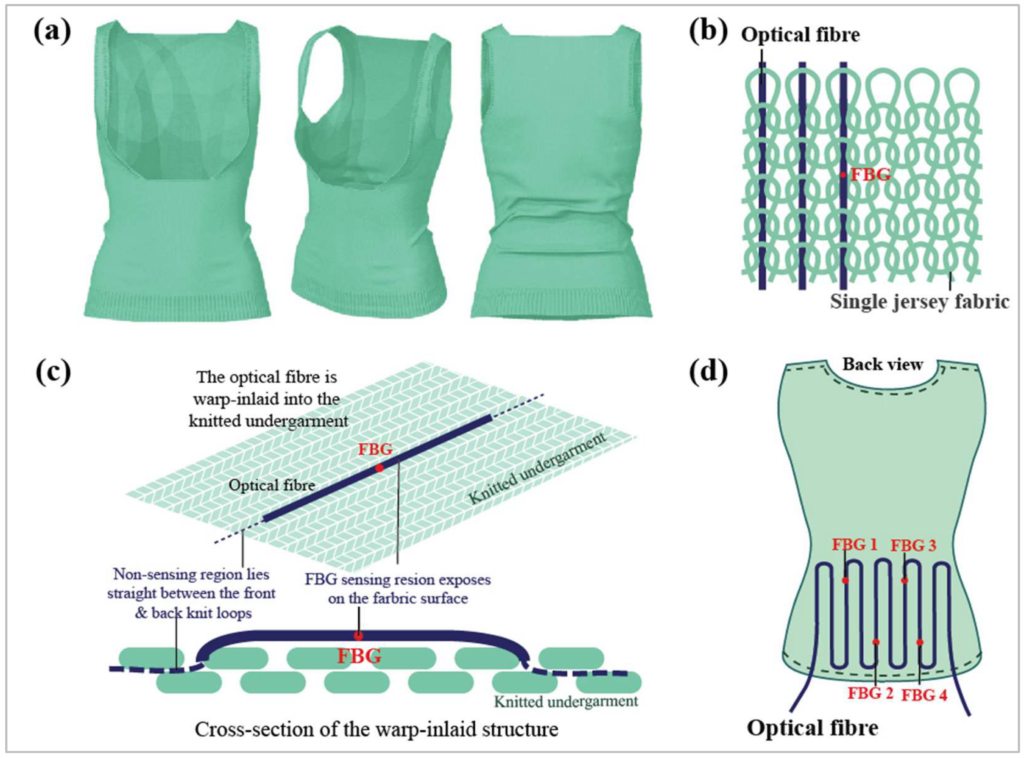
A Novel Force-Sensing Smart Textile: Inserting Silicone-Embedded FBG Sensors into a Knitted Undergarment
This study presents a novel method for developing force-sensing smart textiles by embedding silicone-enclosed fiber Bragg grating sensors. The innovation enhances sensitivity, flexibility, and real-time data acquisition, aiding in precise bracing treatments for scoliosis, with promising accuracy and adaptability. Read more
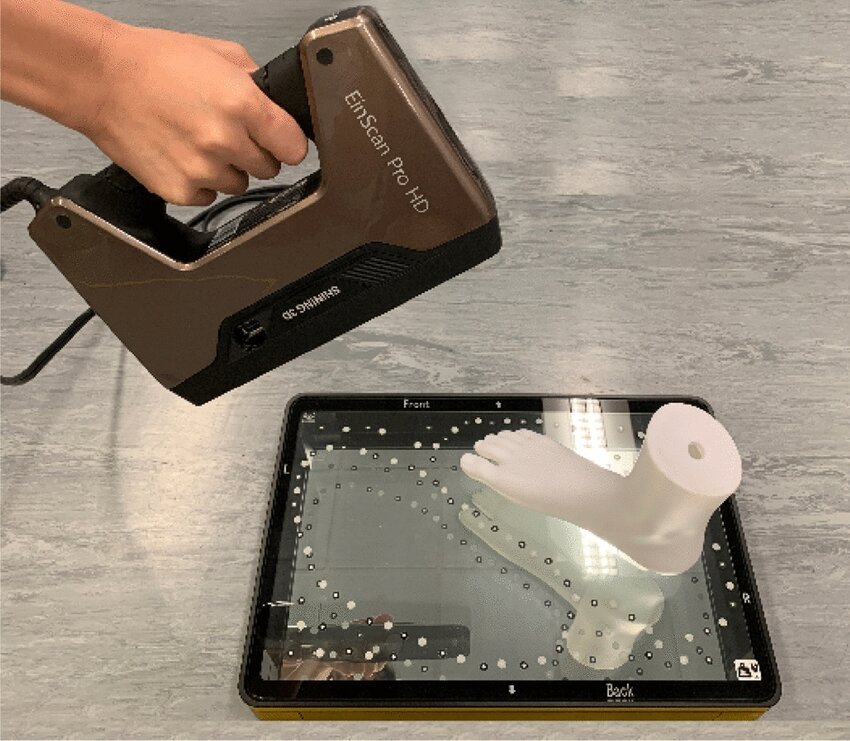
An exploratory study of dynamic foot shape measurements with 4D scanning system
This study uses a 4D foot scanning system to analyze foot deformation in diabetic patients, focusing on dynamic shape changes during walking. By employing point cloud registration and measurement extraction algorithms, it aims to enhance insole and footwear comfort through improved understanding of foot dynamics. Read more

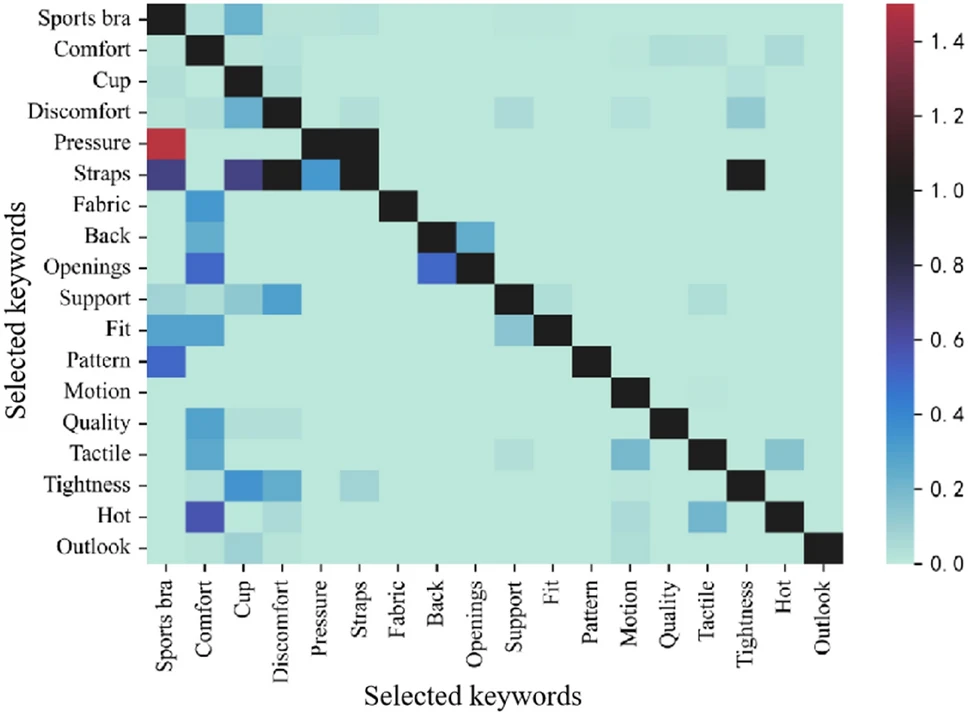
The inter-connection of sports bra design attributes and elderly women’s perceptions
This study explores sports bra design for elderly women, focusing on comfort through support, cup design, and thermal management. Network analysis reveals discomfort links to tightness and straps, guiding improvements for age-friendly sportswear. Read more
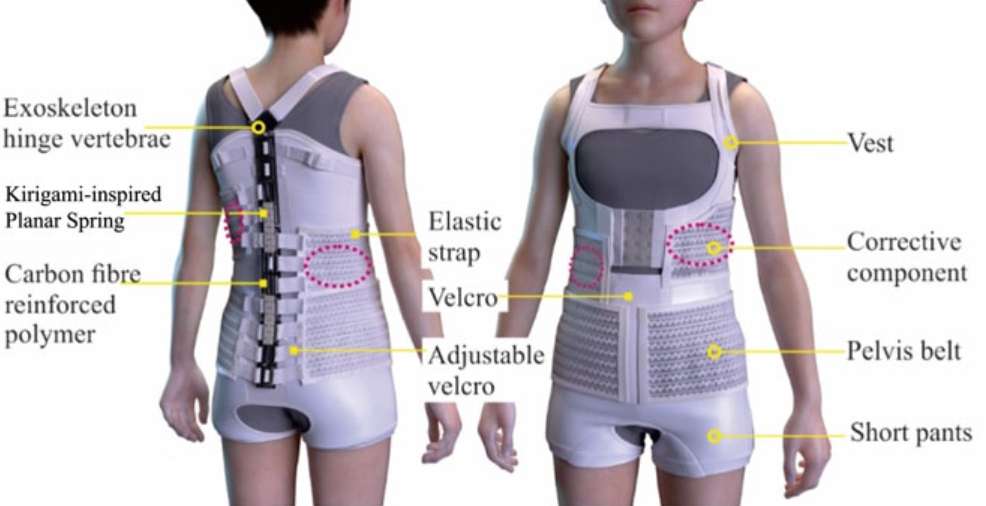
Design and characterize of kirigami-inspired springs and the application in vertebrae exoskeleton for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis brace treatment
Kirigami-inspired springs, optimized via additive manufacturing and FEM, enhance scoliosis treatment with carbon-fiber-reinforced nylon. They offer comfort and effective spinal correction, showing 4.6% to 50.5% improvement in Cobb angle without obstructing X-ray views. Read more
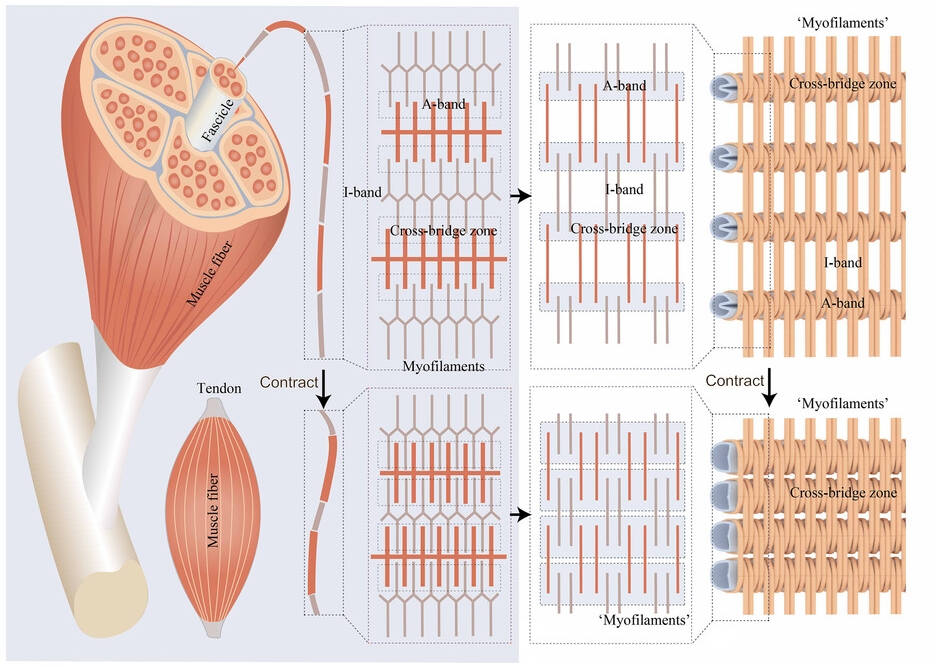
Fluid‐Driven High‐Performance Bionic Artificial Muscle with Adjustable Muscle Architecture
Fluid-Driven ExoMuscle mimics sarcomere structures with adjustable architecture, achieving up to 0.9 MPa actuation stress and 10.94 kW/kg power density. This bionic muscle enhances bio-robotics and wearable robots, combining efficiency with adaptability to human anatomy. Read more
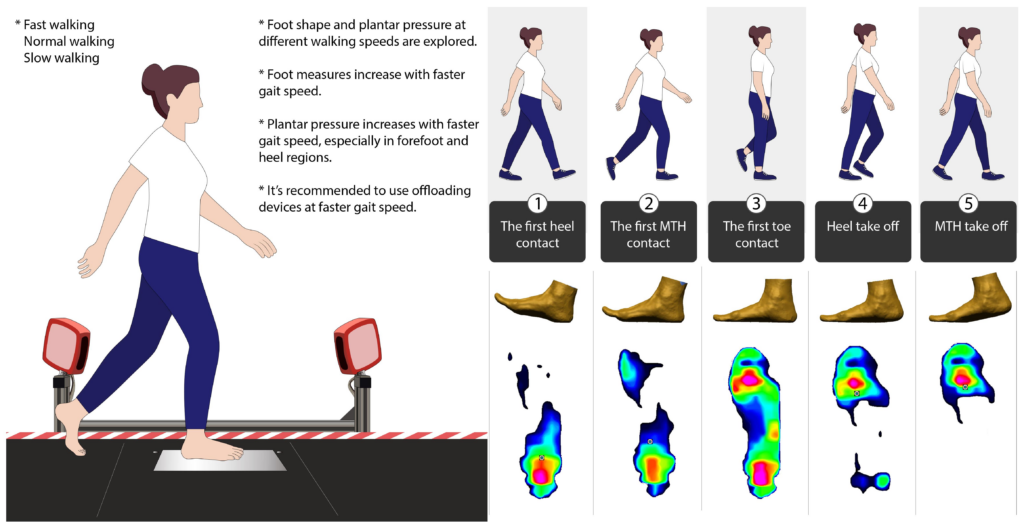
Analysis of Diabetic Foot Deformation and Plantar Pressure Distribution of Women at Different Walking Speeds
This study analyzes foot deformation and plantar pressure in diabetic patients at varying walking speeds. It shows increased pressure in forefoot and heel at higher speeds, stressing the need for suitable footwear and offloading devices to protect against injury and ensure comfort. Read more
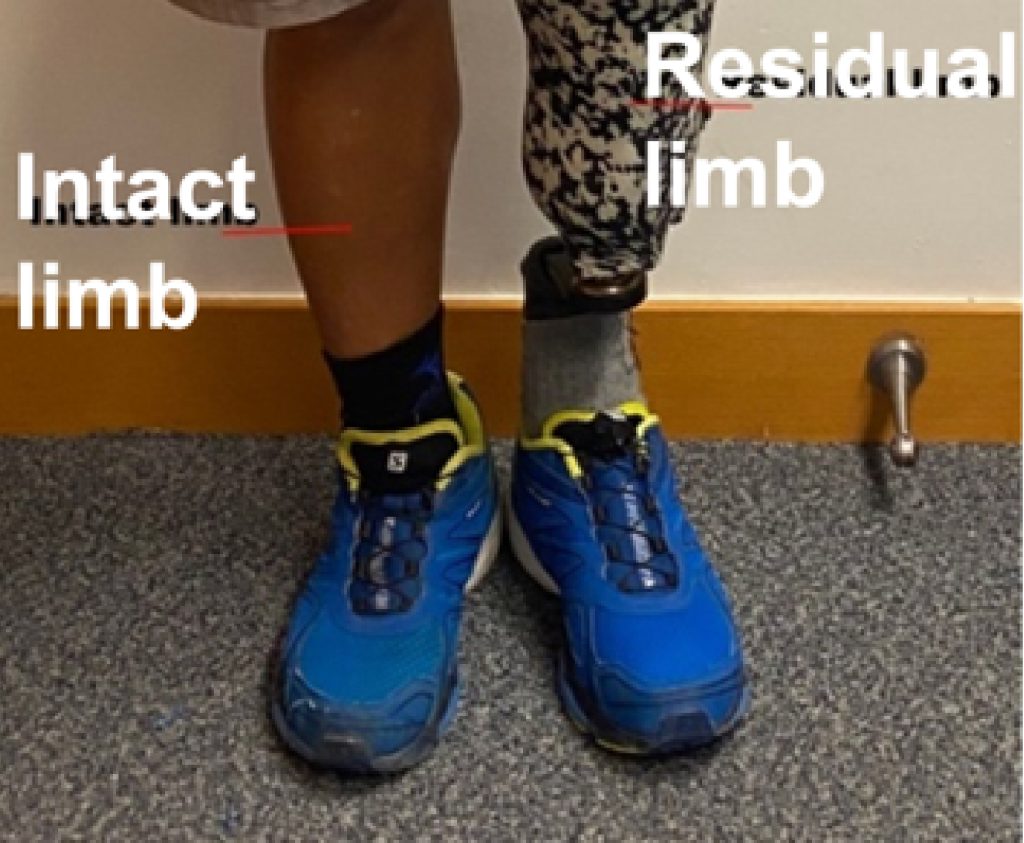
Biomechanical Analysis Of Unilateral Transtibial Amputees Using Prosthetic Foot During Treadmill Walking At Varying Slopes: 1721
This study aimed to investigate the effect of the prosthetic foot used by unilateral transtibial amputees during different walk tasks by utilizing biomechanical analysis. Read more
Surface electromyography (sEMG) biofeedback posture training improves the physical and mental health of early adolescents with mild scoliosis: A qualitative study
This study explores a biofeedback posture training program for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, highlighting its ability to improve paraspinal muscle symmetry and reduce curve progression. It also examines how the program enhances posture correction and quality of life for adolescents through subjective experiences. Read more

Optimization of amino acid-based poly(ester urea urethane) nanoparticles for the systemic delivery of gambogic acid for treating triple negative breast cancer
The study investigates the structure–property relationship by fine-tuning the structure of AA-PEUU, including the amino acid type, hydrocarbons, the ratio of functional building blocks, and PEGylation, to identify the nanoparticle candidate with optimized delivery performances. Read more

Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
