Publications
Filter
Year
The relevance of breast motions and gaits in running exercises
This study predicts breast motion using gait parameters for sports bra evaluation, employing neural networks and optimization algorithms. Findings reveal significant motion diversity in breast regions and a moderate correlation with gait, enhancing comfort and functionality assessments. Read more

Selection of breast features for young women in northwestern China based on the random forest algorithm
This study utilizes the random forest algorithm to optimize breast feature selection, enhancing classification accuracy. By ranking feature importance, it identifies key variables, using clustering and neural networks, showing that fewer features improve shape recognition efficiency. Read more

Immediate Effects of Posture Correction Girdle on Adolescents with Early Scoliosis.
This study explores a posture correction girdle for adolescents with early scoliosis, using radiographic imaging and 3D body scanning. Findings reveal positive effects, including reduced spinal curves and improved postural balance, suggesting alternative treatment options beyond observation. Read more

A zwitterionic silver nanoparticle-incorporating injectable hydrogel with a durable and efficient antibacterial effect for accelerated wound healing
Antibacterial wound dressing is essential for inflammation control and accelerated wound healing. This study investigates polyzwitterion-functionalized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with enhanced antibacterial performance in an injectable wound dressing hydrogel. Read more

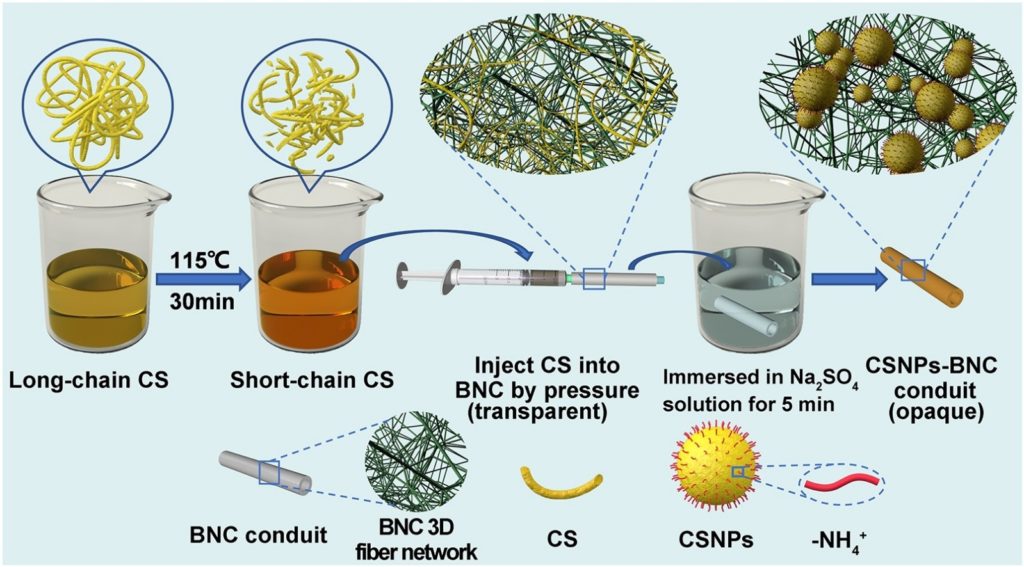
A novel approach for efficient fabrication of chitosan nanoparticles-embedded bacterial nanocellulose conduits
This study introduces a method to embed chitosan nanoparticles in bacterial nanocellulose, enhancing antibacterial properties and biocompatibility. Utilizing ionic gelation, the composite supports Schwann cell growth, showcasing its potential for clinical biomedical applications. Read more
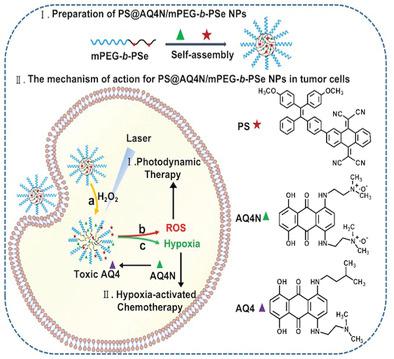
ROS‐responsive selenium‐containing carriers for coencapsulation of photosensitizer and hypoxia‐activated prodrug and their cellular behaviors
This study explores integrating hypoxia-activated chemotherapy with photodynamic therapy via ROS-responsive drug carriers. The method enhances drug release, showing significant tumor treatment efficacy, indicating promising advancements in cancer therapy approaches. Read more
Can infrared camera images be used for screening in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?
This study explores IR thermography for non-radiation screening of AIS, comparing thermal patterns to spinal deformities on X-rays. Key findings suggest a potential for early detection and severity prediction, providing a safe and automated approach to AIS screening without radiation. Read more

A Novel Bespoke Hypertrophic Scar Treatment: Actualizing Hybrid Pressure and Silicone Therapies with 3D Printing and Scanning
This study presents a novel hypertrophic scar treatment using 3D printing and silicone elastomers. The methodology includes pressure distribution optimization via finite element analysis, resulting in enhanced pressure control on scars, offering improved healing outcomes with a custom-fit design. Read more

Biosafety evaluation and quantitative determination of poly (hexamethylene biguanide) (PHMB) coated on cellulosic fabrics by Kubelka–Munk equation
This study presents a method to quantify cationic finishing agents on cellulosic fabrics using the Kubelka–Munk equation. Findings reveal maximum PHMB adsorption around 8 mg/g and establish a safe, non-cytotoxic PHMB level for biosafety, offering crucial insights for fabric treatment. Read more

Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
Here goes your text ... Select any part of your text to access the formatting toolbar.
